Sooty blotch
In organic apple orchards and orchards with low fungicide input during summer (e.g. orchards of scab resistant varieties and apple cider orchards), infection of fruit with sooty blotch may occur. It is a complex of different fungi that causes black spots on the skin of the fruit. Infections are possible starting from June, but most symptoms do not become visible until late summer.
The video with detailed explanations about this model is available here
The fungi responsible for sooty blotch live on plants around the orchard, as well as on branches and mummified fruit in the orchard. The model assumes the presence of an inexhaustible primary inoculum. From this inoculum, the spores can be sprayed by rain on the fruits.
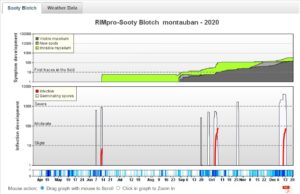
In the bar below the graph, dark blue represents the periods when your weather station recorded rain. Light blue is the period when there is wetness on the leaves, this is calculated based on your records of rain, relative humidity and leaf wetness.
The middle graph shows spore projection by rain (white) and potential infection events (red). The germination process progresses during rain or when leaf wetness or relative humidity is high.
The upper graph shows the incubation period (green) and the period from which symptoms become visible and develop on the fruits (grey and black). The fungus grows on the surface of the fruit and becomes visible when the mycelium changes color from transparent to olive grey. The time between infection and the appearance of the first visible symptoms seems to be related to the number of hours of wetness and independent of temperature. Disease incidence (= number of infected fruits) increases during summer with infections caused by spores from both primary and secondary sources.
Get in touch
You can set up your account and your stations yourself online on our website. Do you have any questions, or do you need assistance? Please contact us.